背景
在Arm64多核处理器中, 各核间的关系可能不同. 比如1个16 core的cpu, 每4个core划分为1个cluster,共享L2 cache. 当我们需要从core 0将任务调度出来时,如果优先选择core 1~3, 那么性能明显时优于其他core的.
那么操作系统怎么知道core之间这样的拓扑信息呢? Arm提供了MPIDR_EL1 寄存器. 每个core都有一个该寄存器。
字段说明
a.该寄存器为只读寄存器
b.AFF3 & AFF2 都为ClusterID(从软件角度理解为不同CPU组的ID),AFF1 为CPUID,AFF0 为多线程核的线程ID(指的是是否支持超线程的id)
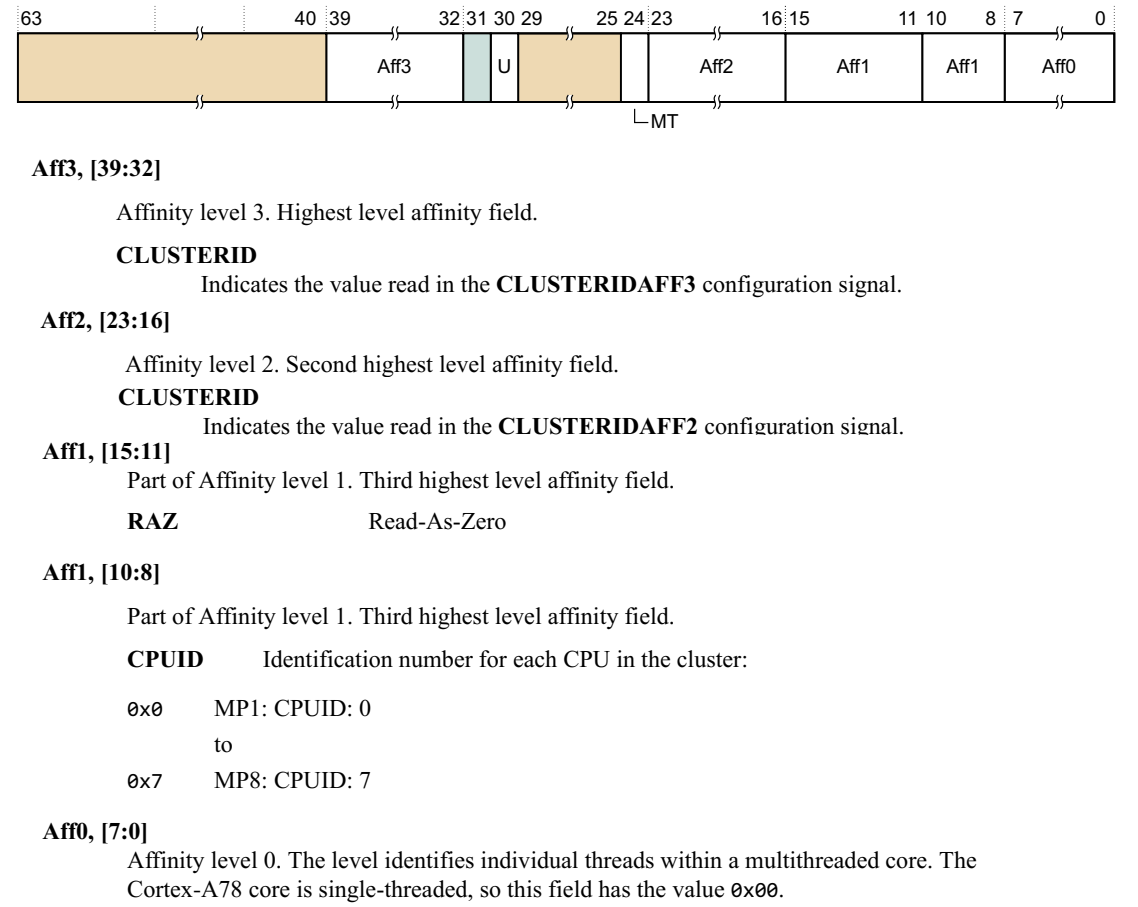
MPIDR_EL1
U, bit [30]
0表示多核处理, 1表示单核处理
MT, bit [24]
0表示没有使用单核超线程, 1表示使用了单核超线程。
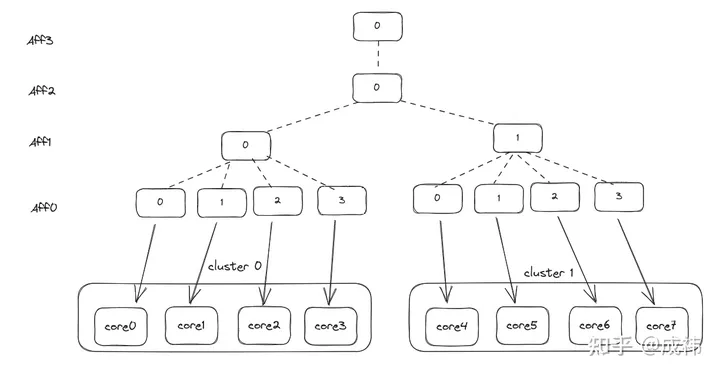
其他的affinity,则表示了各核之间的亲和性。以一个8核2 cluster 非超线程cpu为例, core0的mpidr_el1的affinity为(0,0,0,0),core1为(0,0,0,1),以次类推, core7则为(0,0,1,3)。Arm规范要求了每个core的(Aff3,Aff2,Aff1,Aff0)编码必须唯一。不支持超线程的cpu, Aff0表示核id
这样通过树形结构的编码,OS可以从该寄存器中获取各core之间的关系。
kernel 应用
// kernel表示每个core的拓扑结构,每个core对应一个该结构
struct cpu_topology {
int thread_id;
int core_id;
int package_id;
int llc_id;
cpumask_t thread_sibling;
cpumask_t core_sibling;
cpumask_t llc_sibling;
};
void store_cpu_topology(unsigned int cpuid)
{
struct cpu_topology *cpuid_topo = &cpu_topology[cpuid];
// 读取MPIDR_EL1
u64 mpidr = read_cpuid_mpidr();
/* Create cpu topology mapping based on MPIDR. */
// 判断芯片是否支持超线程
if (mpidr & MPIDR_MT_BITMASK) {
/* Multiprocessor system : Multi-threads per core */
// 在支持超线程的cpu, Aff0表示一个core内的超线程id
cpuid_topo->thread_id = MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(mpidr, 0);
cpuid_topo->core_id = MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(mpidr, 1);
// package_id即cluster id
cpuid_topo->package_id = MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(mpidr, 2) |
MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(mpidr, 3) << 8;
} else {
/* Multiprocessor system : Single-thread per core */
cpuid_topo->thread_id = -1;
// 不支持超线程的cpu, Aff0表示核id
cpuid_topo->core_id = MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(mpidr, 0);
cpuid_topo->package_id = MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(mpidr, 1) |
MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(mpidr, 2) << 8 |
MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(mpidr, 3) << 16;
}
... ...
}MPIDR_EL1在devicetree中的体现
配置DTS时,需要设置MPIDR_EL1的值到CPU node中的reg property,以ArmV8 64bit系统为例:当#address-cell property为2时,需要设置MPIDR_EL1[39:32]到第一个reg cell的reg[7:0]、MPIDR_EL1[23:0]到第二个reg celll的reg[23:0]; 当#address-cellproperty为1时,需要设置MPIDR_EL1[23:0]到reg[23:0];reg的其他位设置位0。
Linux启动过程中MPIDR_EL1的相关逻辑
a.内核中定义了cpu的逻辑映射变量如下,该变量保存MPIDR_EL1寄存器中亲和值。
/* * Logical CPU mapping. */
extern u64 __cpu_logical_map[NR_CPUS];
#define cpu_logical_map(cpu) __cpu_logical_map[cpu]
b.cpu0(boot cpu/primary cpu)获取mpidr_el1亲和值的方式与其他cpu(secondary cpu)
获取方式有所不同。
void __init smp_setup_processor_id(void)
{
/*启动该过程时只有boot cpu即cpu0在执行,其他cpu还未启动
通过read_cpuid_mpidr获取的MPIDR_EL1值即为当前执行的CPU0
的亲和值*/
u64 mpidr = read_cpuid_mpidr() & MPIDR_HWID_BITMASK;
/*将获取到的cpu0的亲和值保存在cpu_logical_map(0)*/
cpu_logical_map(0) = mpidr;
/*
* clear __my_cpu_offset on boot CPU to avoid hang caused by
* using percpu variable early, for example, lockdep will
* access percpu variable inside lock_release
*/
set_my_cpu_offset(0);
pr_info("Booting Linux on physical CPU 0x%lx\n", (unsigned long)mpidr);
}

评论 (0)