本文基于以下软硬件假定:
架构:AARCH64
软件:Uboot 2021.10-rc1
1. Linux启动基础镜像
uboot主要用于启动操作系统,以armv8架构下的linux为例,其启动时需要包含kernel、dtb和rootfs三部分。uboot镜像都是以它们为基础制作的,因此在介绍uboot镜像格式之前我们需要先了解一下它们的构成。
1.1 内核镜像
1.1.1 vmlinux镜像
linux内核编译完成后会在根目录生成原始的内核文件为vmlinux,使用readelf工具可看到其为elf文件格式:
lgj@ubuntu:~/work/linux$ readelf -h vmlinux
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF64
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: DYN (Shared object file)
Machine: AArch64
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0xffff800010000000
Start of program headers: 64 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 13681696 (bytes into file)
Flags: 0x0
Size of this header: 64 (bytes)
Size of program headers: 56 (bytes)
Number of program headers: 3
Size of section headers: 64 (bytes)
Number of section headers: 29
Section header string table index: 28由于uboot引导的镜像不能包含elf头,因此该镜像不能直接被uboot使用。
1.1.2 Image和zImage镜像
Image镜像是vlinux经过objcopy去头后生成的纯二进制文件,对于armv8架构其编译的Makefile如下:
OBJCOPYFLAGS_Image := -O binary -R .note -R .note.gnu.build-id -R .comment –S (1)
targets := Image Image.bz2 Image.gz Image.lz4 Image.lzma Image.lzo
$(obj)/Image: vmlinux FORCE
$(call if_changed,objcopy) (2)
$(obj)/Image.bz2: $(obj)/Image FORCE
$(call if_changed,bzip2) (3)
$(obj)/Image.gz: $(obj)/Image FORCE
$(call if_changed,gzip) (4)
$(obj)/Image.lz4: $(obj)/Image FORCE
$(call if_changed,lz4) (5)
$(obj)/Image.lzma: $(obj)/Image FORCE
$(call if_changed,lzma) (6)
$(obj)/Image.lzo: $(obj)/Image FORCE
$(call if_changed,lzo) (7)(1)objcopy命令使用的flag定义
(2)以vmlinux为原始文件,通过objcopy命令制作Image镜像。其命令可扩展如下:
aarch64-linux-gnu-objcopy -O binary -R .note -R .note.gnu.build-id -R .comment -S vmlinux Image该命令会执行以下操作:
a –O binary:将输出二进制镜像,即会去掉elf头
b –R .note:-R选项表示去掉镜像中指定的section,如这里会去掉.note、.note.gnu.build-id和.comment段
c –S:去掉符号表和重定位信息,它与-R选项的功能类似,都是为了减小镜像的size
因此,执行该命令后生成的Image镜像是去掉elf头,去掉.note等无用的section,以及strip过的二进制镜像。它可以被uboot的booti命令直接启动。但若要使用bootm启动,则还需要将其进一步封装为后面介绍的uimage或bootimg镜像
(3 – 7)以Image为源文件,调用不同的压缩算法,对镜像进行压缩。若调用gzip命令,则可将其压缩为我们熟悉的zImage镜像。与Image一样,压缩后的镜像也是可以被booti直接启动,且经过封装以后可以被bootm启动的
1.2 设备树
设备树是设备树dts源文件经过编译后生成的,其目标文件为二进制格式的dtb文件。其示例编译命令如下:
dtc -I dts -O dtb -o example.dtb example.dts
(1) –I:指定输入文件格式
(2)–O:指定输出文件格式
(3)–o:指定输出文件名
设备树还支持dtb overlay机制,即可以向设备提供一个基础dtb和多个dtbo镜像,并在启动前将它们merge为最终的dtb。下面用一个例子来说明:
(1)基础dts文件base.dts内容如下:
/dts-v1/;
/ {
foo: foonode {
foo-property;
};
};(2)dtbo源文件overlay.dts内容如下:
/dts-v1/;
/plugin/;
/ {
fragment@1 {
target = <&foo>;
__overlay__ {
overlay-1-property;
bar: barnode {
bar-property;
};
};
};
};(3)分别使用以下命令编译dtb和dtbo
dtc -@ -I dts -O dtb -o base.dtb base.dts
dtc -@ -I dts -O dtb -o overlay.dtbo overlay.dts(4)将dtbo merge到base dtb上
a 通过fit镜像包含和定义一个overlay,这种情况uboot会自动解析fit参数并执行merge操作
b 手动加载和apply overlay
(5)手动merge流程
a 设置base dtb和dtbo的地址
setenv fdtaddr 0x87f00000
setenv fdtovaddr 0x87fc0000b 加载base dtb和dtbo
load ${devtype} ${bootpart} ${fdtaddr} ${bootdir}/base.dtb
load ${devtype} ${bootpart} ${fdtovaddr} ${bootdir}/overlay.dtboc 将base dtb设置为工作dtb
fdtaddr $fdtaddrd 增大dtb的size,以使其可以容纳所有overlay
fdt resize 8192e apply dtb overlay
fdt apply $fdtovaddr1.3 根文件系统
linux可以支持多种形式的根文件系统,如initrd、initramfs、基于磁盘的根文件系统等。站在启动镜像的角度看其实它们都是制作好的文件系统镜像,内核可以从特定的位置获取并挂载它们。以下是它们在启动时的基本特性:
(1)initrd
它是一种内存文件系统,需要由bootloader预先加载到内存中,并将其内存地址传递给内核。如uboot将initrd加载到地址$initrd_addr处,则bootm参数如下:
bootm $kernel_addr $initrd_addr $fdt_addr
(2)initramfs
initramfs也是一种内存文件系统,但与initrd不同,它是与内核打包在一起的。因此不需要通过额外的参数
(3)磁盘rootfs
磁盘根文件系统会被刷写到flash、mmc或disk的分区中,在内核启动时可在bootargs添加下面格式的参数,以指定根文件系统的位置
root=/dev/xxx
因此,以上这些rootfs只有initrd是需要uboot独立加载的,故只有当rootfs为initrd时,uboot镜像打包流程才需要在镜像打包时为其单独考虑
2. Uboot支持的镜像格式
2.2 Legacy uimage格式
uboot最先支持legacy uimage格式的镜像,它是在内核镜像基础上添加一个64字节header生成的。该header信息用于指定镜像的一些属性,如内核的类型、压缩算法类型、加载地址、运行地址、crc完整性校验值等。其格式如下:
typedef struct image_header {
uint32_t ih_magic; /* Image Header Magic Number */
uint32_t ih_hcrc; /* Image Header CRC Checksum */
uint32_t ih_time; /* Image Creation Timestamp */
uint32_t ih_size; /* Image Data Size */
uint32_t ih_load; /* Data Load Address */
uint32_t ih_ep; /* Entry Point Address */
uint32_t ih_dcrc; /* Image Data CRC Checksum */
uint8_t ih_os; /* Operating System */
uint8_t ih_arch; /* CPU architecture */
uint8_t ih_type; /* Image Type */
uint8_t ih_comp; /* Compression Type */
uint8_t ih_name[IH_NMLEN]; /* Image Name */
} image_header_t;uboot的bootm命令会解析镜像头中的信息,并根据这些信息执行镜像校验、解压和启动等流程。以下是创建uImage的命令示例:
mkimage -A arm64 -O linux -C none -T kernel -a 0x80008000 -e 0x80008040 -n Linux_Image -d zImage uImage但是它也有着一些缺点,如:
(1)加载流程比较繁琐,如需要分别加载内核、initrd和dtb
(2)启动参数较多,需要分别制定内核、initrd和dtb的地址
(3)在支持secure boot的系统中对secure boot的支持不足
为此,uboot又定义了一种新的镜像格式fit uimage,用于解决上述问题
2.2 Fit uimage格式
Fit uimage是使用devicetree语法来定义uimage镜像描述信息以及启动时的各种属性,这些信息被写入一个后缀名为its的源文件中。以下是一个its文件的示例
/dts-v1/;
/ {
description = "Various kernels, ramdisks and FDT blobs";
#address-cells = <1>;
images {
kernel-1 {
description = "vanilla-2.6.23"; (1)
data = /incbin/("./vmlinux.bin.gz"); (2)
type = "kernel"; (3)
arch = "ppc"; (4)
os = "linux"; (5)
compression = "gzip"; (6)
load = <00000000>; (7)
entry = <00000000>; (8)
hash-1 {
algo = "md5"; (9)
};
hash-2 {
algo = "sha1";
};
};
kernel-2 {
description = "2.6.23-denx";
data = /incbin/("./2.6.23-denx.bin.gz");
type = "kernel";
arch = "ppc";
os = "linux";
compression = "gzip";
load = <00000000>;
entry = <00000000>;
hash-1 {
algo = "sha1";
};
};
kernel-3 {
description = "2.4.25-denx";
data = /incbin/("./2.4.25-denx.bin.gz");
type = "kernel";
arch = "ppc";
os = "linux";
compression = "gzip";
load = <00000000>;
entry = <00000000>;
hash-1 {
algo = "md5";
};
};
ramdisk-1 {
description = "eldk-4.2-ramdisk";
data = /incbin/("./eldk-4.2-ramdisk");
type = "ramdisk";
arch = "ppc";
os = "linux";
compression = "gzip";
load = <00000000>;
entry = <00000000>;
hash-1 {
algo = "sha1";
};
};
ramdisk-2 {
description = "eldk-3.1-ramdisk";
data = /incbin/("./eldk-3.1-ramdisk");
type = "ramdisk";
arch = "ppc";
os = "linux";
compression = "gzip";
load = <00000000>;
entry = <00000000>;
hash-1 {
algo = "crc32";
};
};
fdt-1 {
description = "tqm5200-fdt";
data = /incbin/("./tqm5200.dtb");
type = "flat_dt";
arch = "ppc";
compression = "none";
hash-1 {
algo = "crc32";
};
};
fdt-2 {
description = "tqm5200s-fdt";
data = /incbin/("./tqm5200s.dtb");
type = "flat_dt";
arch = "ppc";
compression = "none";
load = <00700000>;
hash-1 {
algo = "sha1";
};
};
};
configurations {
default = "config-1";
config-1 {
description = "tqm5200 vanilla-2.6.23 configuration";
kernel = "kernel-1";
ramdisk = "ramdisk-1";
fdt = "fdt-1";
};
config-2 {
description = "tqm5200s denx-2.6.23 configuration";
kernel = "kernel-2";
ramdisk = "ramdisk-1";
fdt = "fdt-2";
};
config-3 {
description = "tqm5200s denx-2.4.25 configuration";
kernel = "kernel-3";
ramdisk = "ramdisk-2";
};
};
};它包含images和configurations两个顶级节点,images指定该its文件会包含哪些镜像,以及这些镜像的属性信息。configurations用于定义一系列镜像组合信息,如在本例中包含了config-1、config-2和config-3三种镜像组合方式。Its使用default属性指定启动时默认采用的配置信息,若启动时不希望使用默认配置,则可通过在启动参数中动态指定配置序号。下面我们通过kernel-1节点看下image属性的含义:
(1)镜像的描述信息
(2)镜像文件的路径
(3)镜像类型,如kernel、ramdisk或fdt
(4)支持的架构
(5)支持的操作系统
(6)其使用的压缩算法
(7)加载地址
(8)运行地址
(9)完整性校验使用的hash算法
configurations的属性比较简单,就是指定某个配置下使用哪一个kernel、dtb和ramdisk镜像。Fit image除了支持完整性校验外,还可支持hash算法 + 非对称算法的secure boot方案,如以下例子:
kernel {
data = /incbin/("test-kernel.bin");
type = "kernel_noload";
arch = "sandbox";
os = "linux";
compression = "none";
load = <0x4>;
entry = <0x8>;
kernel-version = <1>;
signature {
algo = "sha1,rsa2048"; (1)
key-name-hint = "dev"; (2)
};
};(1)指定sha1为secure boot签名使用的hash算法,rsa2048为其使用的签名算法
(2)可能使用的验签密钥名
与设备树类似,its文件可以通过mkimage和dtc编译生成itb文件。镜像生成方式如下:
mkimage -f xxx.its xxx.itbxxx.itb文件可以直接传给uboot,并通过bootm命令执行,如xxx.itb被加载到0x80000000,则其命令如下:
bootm 0x80000000
若需要选择非默认的镜像配置,则可通过指定配置序号实现,例如:
bootm 0x80000000#config@22.3 Boot image格式
boot image是android定义的启动镜像格式,到目前为止一共定义了三个版本(v0 – v2),其中v0版本包含andr_img_hdr、kernel、ramdisk和second stage,v1版本增加了recovery dtbo/acpio,v2版本又增加了dtb。在这些镜像中second stage是可选的,而recovery dtbo只有在使用recovery分区的非AB系统中才需要,且它们都需要page对齐(通常为2k)。以下是boot image镜像的基本格式:
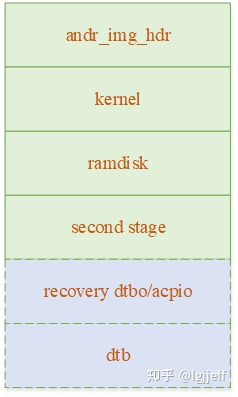
andr_img_hdr镜像头用于描述这些镜像的信息,如其长度、加载地址等,其定义如下:
struct andr_img_hdr {
/* Must be ANDR_BOOT_MAGIC. */
char magic[ANDR_BOOT_MAGIC_SIZE];
u32 kernel_size; /* size in bytes */
u32 kernel_addr; /* physical load addr */
u32 ramdisk_size; /* size in bytes */
u32 ramdisk_addr; /* physical load addr */
u32 second_size; /* size in bytes */
u32 second_addr; /* physical load addr */
u32 tags_addr; /* physical addr for kernel tags */
u32 page_size; /* flash page size we assume */
u32 header_version;
u32 os_version;
char name[ANDR_BOOT_NAME_SIZE]; /* asciiz product name */
char cmdline[ANDR_BOOT_ARGS_SIZE];
u32 id[8]; /* timestamp / checksum / sha1 / etc */
char extra_cmdline[ANDR_BOOT_EXTRA_ARGS_SIZE];
u32 recovery_dtbo_size; /* size in bytes for recovery DTBO/ACPIO image */
u64 recovery_dtbo_offset; /* offset to recovery dtbo/acpio in boot image */
u32 header_size;
u32 dtb_size; /* size in bytes for DTB image */
u64 dtb_addr; /* physical load address for DTB image */
} __attribute__((packed));可以使用mkbootimg.py脚本制作boot image镜像,该脚本参数比较简单,就是指定与镜像头中定义的相关参数。例如:
mkbootimg.py \
--base aaa \
--kernel kernel/arch/arm64/boot/Image.gz \
--kernel_offset bbb \
--second kernel/arch/arm64/boot/ccc.dtb \
--second_offset ddd \
--board test_board \
-o boot.img3. bootm流程
bootm是uboot用于启动操作系统的命令,它的主要流程包括根据镜像头获取镜像信息,解压镜像,以及启动操作系统。以下为其主要执行流程:
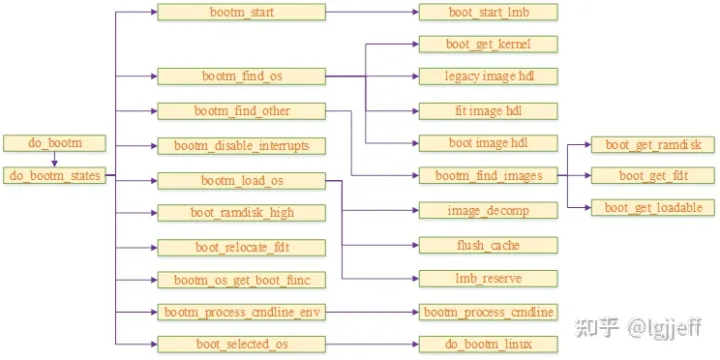
以上流程最终会调用特定os的启动函数,例如需要启动armv8架构的linux,则其调用的接口为arch/arm/lib/bootm.c中的do_bootm_linux。以下为其执行流程:
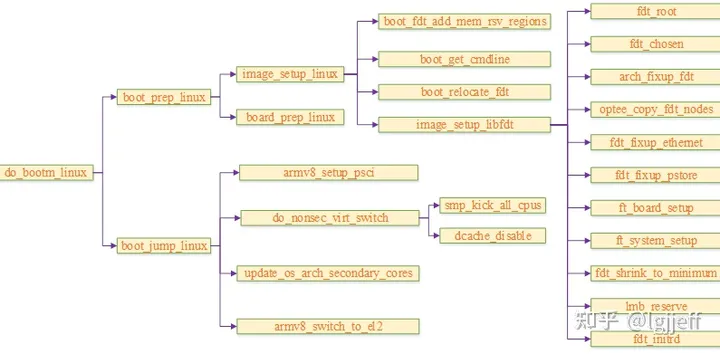
上面的流程都比较直观,有兴趣的同学可以对照代码自行分析一下


评论 (0)